What Does A Grace Period Mean In Finance
adminse
Mar 29, 2025 · 8 min read
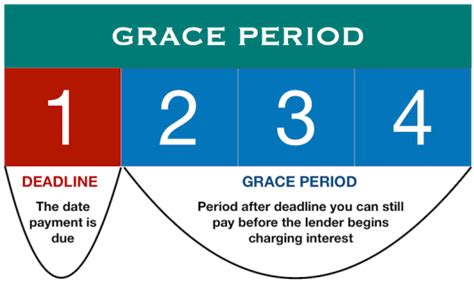
Table of Contents
Decoding the Grace Period: A Comprehensive Guide to Financial Grace
What's the secret to avoiding late fees and maintaining a healthy financial standing? It's often simpler than you think: understanding and utilizing grace periods.
Grace periods are lifelines in the financial world, offering a crucial buffer against penalties and negative impacts on credit scores.
Editor's Note: This comprehensive guide to grace periods in finance was published today. It provides a detailed explanation of what a grace period entails, its various applications, and how to best leverage this valuable financial tool.
Why Grace Periods Matter
In the fast-paced world of finance, unforeseen circumstances can easily disrupt even the most meticulous budgeting. Missed payments, delayed invoices, and unexpected expenses are commonplace. This is where the grace period steps in, acting as a safety net that prevents immediate repercussions for minor, temporary lapses. Understanding and effectively utilizing grace periods can significantly improve your financial health, protecting your credit score, and mitigating potential penalties. From credit cards to loans and insurance premiums, grace periods provide a crucial cushion, allowing you to rectify situations before they escalate into serious financial problems. The impact extends beyond individual finances; understanding grace periods is also crucial for businesses managing cash flow and avoiding late payment penalties.
Overview of this Article
This article delves deep into the multifaceted world of grace periods, exploring their application across various financial products. We'll examine the nuances of grace periods for different financial instruments, explore the implications of missing a grace period, and provide practical tips for maximizing their benefits. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of grace periods and how to leverage them for improved financial management.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the culmination of extensive research, drawing upon data from reputable financial institutions, industry reports, and legal documentation pertaining to consumer credit and lending practices. It incorporates insights from financial experts and analyzes real-world examples to provide a clear and accurate representation of grace periods across different financial contexts.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition of Grace Period | A period of time allowed after a payment due date without penalty. |
| Types of Grace Periods | Vary by financial product (credit cards, loans, insurance, etc.). |
| Implications of Missing | Late fees, negative impact on credit score, potential account closure (depending on the product). |
| Leveraging Grace Periods | Careful budgeting, setting payment reminders, proactive communication with lenders. |
| Grace Period Length | Varies significantly; always check the terms and conditions of your agreement. |
Let's dive deeper into the key aspects of grace periods, starting with their foundational principles and real-world applications.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Grace Periods
-
Grace Period Definitions: A grace period, in its simplest form, is a designated timeframe after a payment's due date during which a payment can be made without incurring penalties. However, the specifics vary significantly depending on the type of financial agreement.
-
Types of Grace Periods: Grace periods aren't uniform across all financial products. Let's examine some key examples:
-
Credit Cards: Credit card grace periods typically apply to purchases, allowing you to avoid interest charges if you pay your balance in full by the due date. However, cash advances usually don't have a grace period, meaning interest accrues immediately. The length of the grace period is typically 21-25 days after the statement closing date.
-
Loans: Loans, such as personal loans, mortgages, or auto loans, may also offer grace periods, though this is less common than with credit cards. These grace periods might be granted under specific circumstances, such as temporary financial hardship, but they're rarely built into the standard loan agreement. Any grace period offered would be at the lender's discretion and usually requires formal application and justification.
-
Insurance Premiums: Insurance policies often include grace periods for premium payments. The length varies by insurer and policy type, but it usually allows a few weeks to make a late payment before the policy lapses. However, coverage may be suspended during the grace period in some cases.
-
Student Loans: Federal student loans typically offer a grace period of six months after graduation or leaving school before repayment begins. This gives borrowers time to find employment and adjust to their post-school financial situation. However, interest may still accrue during this grace period, depending on the loan type.
-
-
Understanding the Implications of Missing a Grace Period: The consequences of failing to make a payment within the grace period vary. Most commonly, it involves:
-
Late Fees: Late payment fees are usually significant and can quickly accumulate if payments are consistently late.
-
Negative Credit Report Impact: Missed payments are reported to credit bureaus, negatively impacting your credit score. This can make it harder to secure loans, rent an apartment, or even get a job in the future.
-
Account Suspension or Closure: Consistent late payments can lead to the suspension or closure of your account, further harming your credit rating and access to financial services.
-
-
Leveraging Grace Periods Effectively: Grace periods are valuable tools, but only if used wisely. Here are some ways to maximize their benefit:
-
Accurate Record Keeping: Maintain a detailed record of all due dates and payment amounts.
-
Payment Reminders: Set up automatic payment reminders or use calendar alerts to avoid missing due dates.
-
Budgeting and Planning: Create a realistic budget and plan your expenses to ensure timely payments.
-
Proactive Communication: If you anticipate difficulties making a payment, contact your lender or provider as soon as possible to discuss options. They may be able to offer a payment plan or extension.
-
-
Grace Period Length Variations: The duration of a grace period is not standardized. It is explicitly defined within the terms and conditions of your specific agreement with the financial institution. Always refer to your contract or statement for the exact details.
Exploring the Connection Between Financial Literacy and Grace Periods
Financial literacy plays a crucial role in effectively utilizing grace periods. Individuals with a strong understanding of personal finance are better equipped to manage their finances, track payments, and avoid situations where grace periods are even necessary. A lack of financial literacy, conversely, can lead to missed payments, late fees, and a damaged credit score. This highlights the importance of ongoing education and proactive financial management. Effective budgeting, understanding interest rates, and setting realistic financial goals are all vital components of utilizing grace periods successfully and avoiding their negative consequences.
Further Analysis of Financial Literacy
| Aspect of Financial Literacy | Impact on Grace Period Utilization | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Budgeting | Prevents missed payments | A well-structured budget helps allocate funds for timely payments, reducing reliance on grace periods. |
| Debt Management | Reduces reliance on grace periods | Effectively managing debt minimizes the chances of missing payments. |
| Understanding Credit Scores | Motivates timely payments | Awareness of the negative impact on credit scores incentivizes prompt payments. |
| Emergency Fund Planning | Mitigates unexpected expenses | An emergency fund can help cover unexpected costs, preventing missed payments. |
FAQ Section
-
Q: What happens if I miss my grace period? A: This can result in late fees, damage to your credit score, and potentially account suspension or closure.
-
Q: Do all financial products offer grace periods? A: No, grace periods are not universally offered. Credit cards commonly provide them, but loans and other financial products may not.
-
Q: How long is a typical grace period? A: The length varies considerably, ranging from a few weeks (for insurance premiums) to a few months (for student loans). Always check your agreement.
-
Q: Can I negotiate an extension beyond the grace period? A: Possibly. Contacting your lender or provider early and explaining your situation might result in a payment arrangement or extension.
-
Q: Does interest accrue during a grace period? A: This depends on the product. Credit card purchases typically don't accrue interest during the grace period if you pay the full balance, but cash advances do. Interest may accrue on some loans during grace periods.
-
Q: How do grace periods impact my credit score? A: Missing payments, even during a grace period, will negatively impact your credit score. Making timely payments, even if within a grace period, positively affects your creditworthiness.
Practical Tips
-
Set up automatic payments: This ensures timely payments and eliminates the risk of forgetting due dates.
-
Use calendar reminders: Set alerts for payment due dates to avoid overlooking them.
-
Create a detailed budget: Allocate funds for all expenses, including loan payments and credit card bills.
-
Monitor your accounts regularly: Stay updated on payment due dates and account balances.
-
Contact your lender proactively: If you anticipate difficulty making a payment, reach out to discuss options.
-
Build an emergency fund: This helps cover unexpected expenses and reduces the likelihood of missed payments.
-
Improve your financial literacy: Understand how different financial products work and the implications of late payments.
-
Review your credit report: Monitor your credit score regularly to track your financial health.
Final Conclusion
Grace periods are a vital element of the financial landscape, providing a buffer against unforeseen circumstances. Understanding how they work, their implications, and how to best utilize them is crucial for maintaining a healthy financial standing. By applying the tips and strategies outlined in this article, individuals and businesses can effectively leverage grace periods, protecting their credit scores and avoiding costly penalties. Proactive financial management, coupled with strong financial literacy, is the key to successfully navigating the world of grace periods and ensuring lasting financial well-being. Remember that while grace periods offer a safety net, responsible financial planning is always the best way to avoid relying on them in the first place. The information provided here should serve as a solid foundation for informed decision-making and the responsible management of your financial obligations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Perkins Loans
Apr 02, 2025
-
Perkins Loan Definition
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum To Pay On A Credit Card
Apr 02, 2025
-
Why Do Credit Cards Have A Minimum Payment
Apr 02, 2025
-
What The Minimum Payment On A Credit Card
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does A Grace Period Mean In Finance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.